EU Stage 5 /
US EPA Tier 4f
1300
mm


Sektörünün En Kârlısı
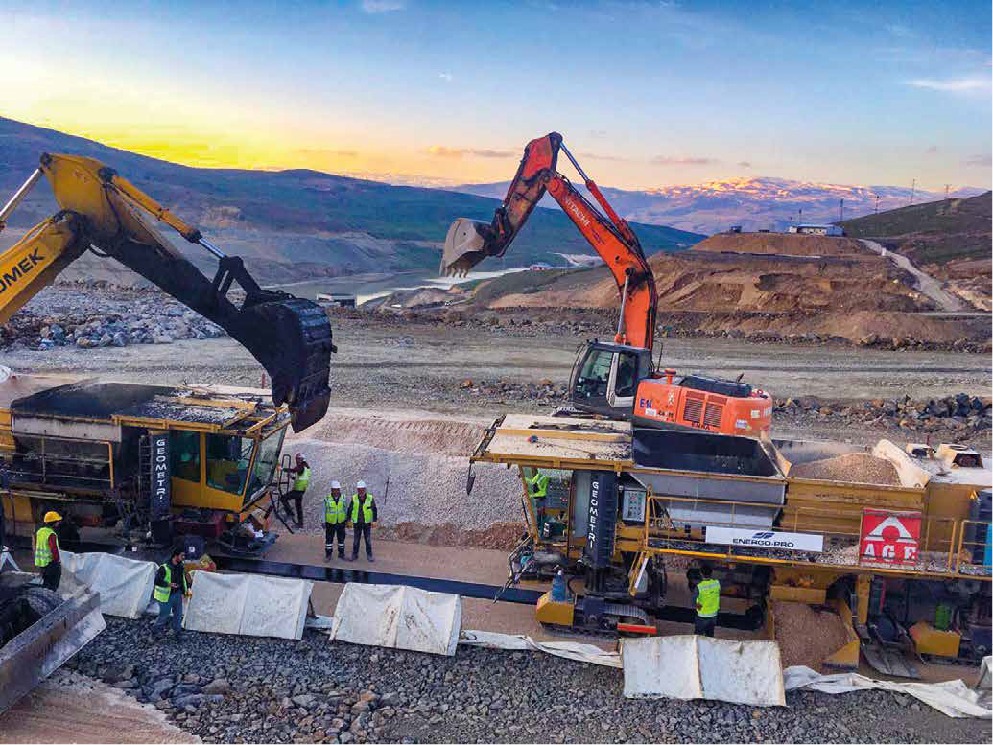
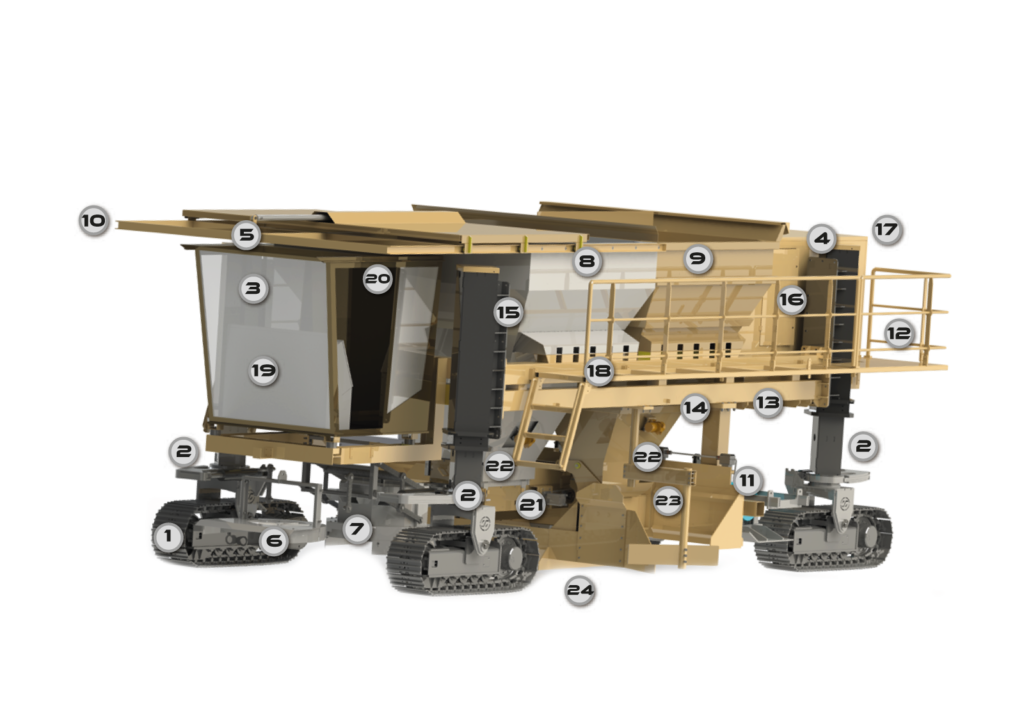
Geometri ACDR X-4 Asfalt Çekirdek Baraj Makinesi, asfalt çekirdekli set barajların inşası için son teknoloji bir inşaat çözümüdür. Geleneksel kil çekirdekli barajların aksine, ACDR X-4, su geçirmez, dayanıklı bir bariyer oluşturmak için yoğun, esnek asfalt beton çekirdek kullanır ve üstün geçirimsizlik, zemin hareketlerine uyum sağlama ve uzun vadeli performans sunar.
With advanced hydraulic automation, integrated compaction, and continuous paving capabilities, the ACDR X-4 ensures efficient, safe, and high-quality dam construction for large-scale infrastructure projects worldwide.
1. Eşzamanlı Katman Yerleştirme
ACDR X-4, 3D baskı sürecine benzer şekilde asfalt çekirdeği ve bitişik geçiş bölgelerini tek geçişte yerleştirebilir, böylece tekdüzelik, hassasiyet ve zaman verimliliği sağlar.
2. Yüksek Yerleştirme Hızı
Modern teknoloji, makinenin günde 750 mm'ye varan hızlarda asfalt çekirdekleri inşa etmesini sağlayarak, yapısal bütünlüğü korurken inşaat sürelerini önemli ölçüde kısaltır.
3. Entegre Sıkıştırma
Dahili titreşimli ve sıkıştırma plakaları ile donatılmış ACDR X-4, asfalt döşendiği sırada sıkıştırarak homojen yoğunluk, yüksek geçirimsizlik ve minimum soğuk derzler sağlar.
4. Hidrolik Kontrol ve Otomasyon
Tamamen hidrolik ve otomatik olan bu sistemde, operatörler gelişmiş bir kontrol panelinden tabaka kalınlığını, genişliğini, eğimini ve sıkıştırma basıncını hassas bir şekilde kontrol edebilir. Bu, dik eğimlerde veya düzensiz baraj profillerinde bile doğru yerleştirme sağlar.
5. Sürekli Çalışma
Makine, barajın uzunluğu boyunca sürekli asfalt serilmesine olanak tanıyarak soğuk derzleri azaltır ve yapının su geçirmezlik bütünlüğünü artırır.
ACDR X-4, aşağıdakileri bir araya getirerek baraj yapımında devrim yaratıyor:
Geometri ACDR X-4 Asfalt Çekirdek Baraj Makinesi ile güven, hız ve hassasiyetle daha güvenli, daha dayanıklı ve çevresel olarak sürdürülebilir barajlar inşa edebilirsiniz.

Asfalt çekirdekli barajlar, özellikle Avrupa ülkelerinde yaygın olan ve şu anda Türkiye'de Kars Karakurt Barajı ve Siirt Çetin Barajı'nda uygulanmakta olan bir baraj türüdür. Bu barajlar, asfaltın düşük geçirgenliği sayesinde su sızıntısını önleyerek kil çekirdekli barajlara kıyasla daha az malzeme kullanımı ve maliyet tasarrufu sağlamaktadır. Ayrıca asfalt döküm süreçlerinin zorlu hava koşullarına dayanıklı olması ve yağmurda dahi devam edebilmesi inşaat zaman kaybını azaltmaktadır. Ancak asfaltın hammaddesinin ithal olması ve yaz aylarında dökümün zor olması gibi dezavantajları da bulunmaktadır. Nevertheless, cost and performance analyses of this dam type suggest that it could be a pioneer for future projects in Turkey
Asfalt çekirdekli barajlar, özellikle Avrupa ülkelerinde yaygın olan ve şu anda Türkiye'de Kars Karakurt Barajı ve Siirt Çetin Barajı'nda uygulanmakta olan bir baraj türüdür. Bu barajlar, asfaltın düşük geçirgenliği sayesinde su sızıntısını önleyerek kil çekirdekli barajlara kıyasla daha az malzeme kullanımı ve maliyet tasarrufu sağlamaktadır. Ayrıca asfalt döküm süreçlerinin zorlu hava koşullarına dayanıklı olması ve yağmurda dahi devam edebilmesi inşaat zaman kaybını azaltmaktadır. Ancak asfaltın hammaddesinin ithal olması ve yaz aylarında dökümün zor olması gibi dezavantajları da bulunmaktadır. Nevertheless, cost and performance analyses of this dam type suggest that it could be a pioneer for future projects in Turkey
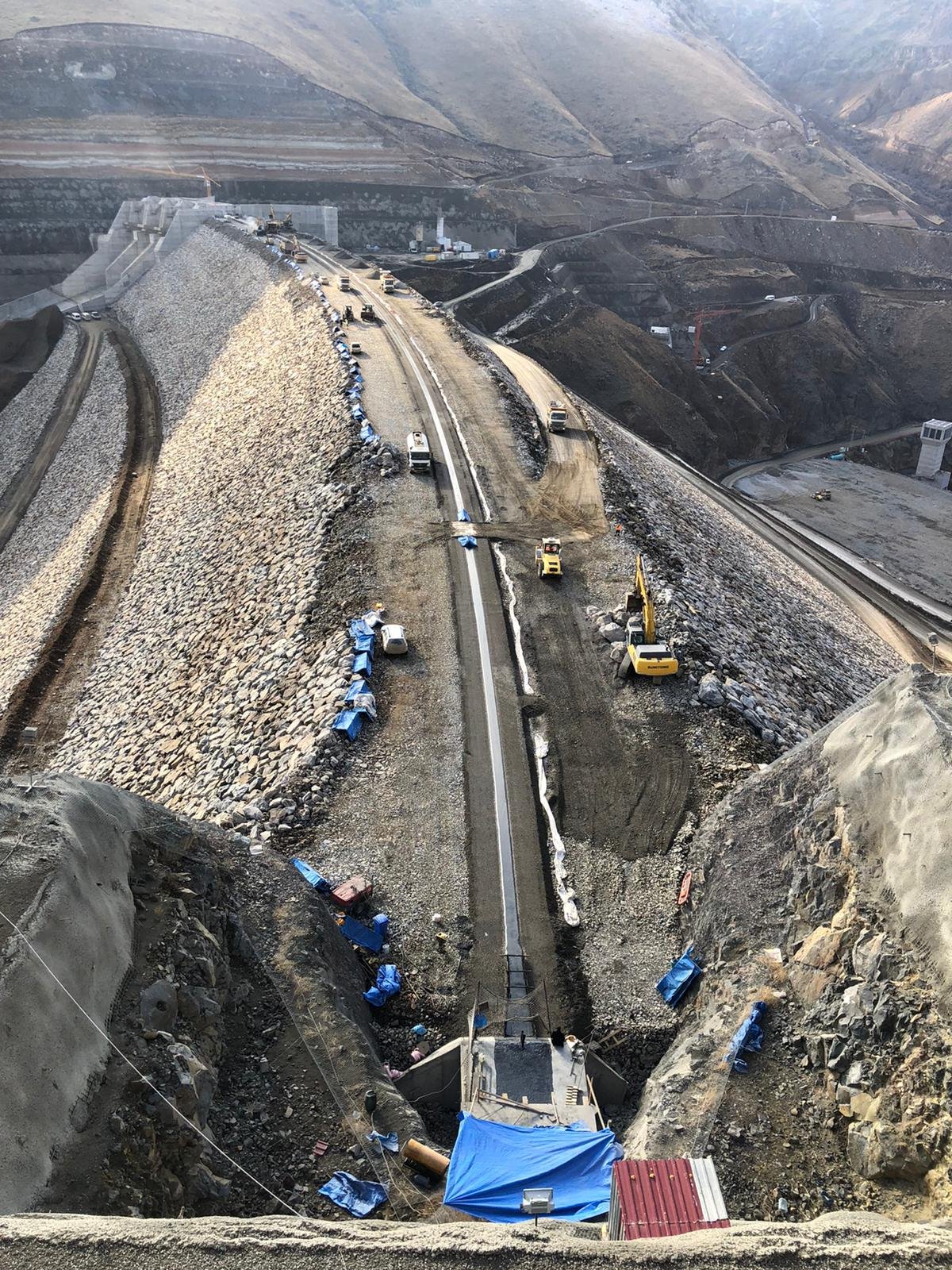

One of the major advantages of these dams is that the permeability is almost zero and much less material is used compared to clay core dams. For example, a clay-core dam basically uses a 25-meter-wide core, whereas with asphalt-core dams this width can be reduced to just 2.05 meters. This results in significant savings in terms of both cost and time. In addition, asphalt paving operations are more resistant to harsher weather conditions and can continue even in light rain. This prevents extended working times and reduces extra costs.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
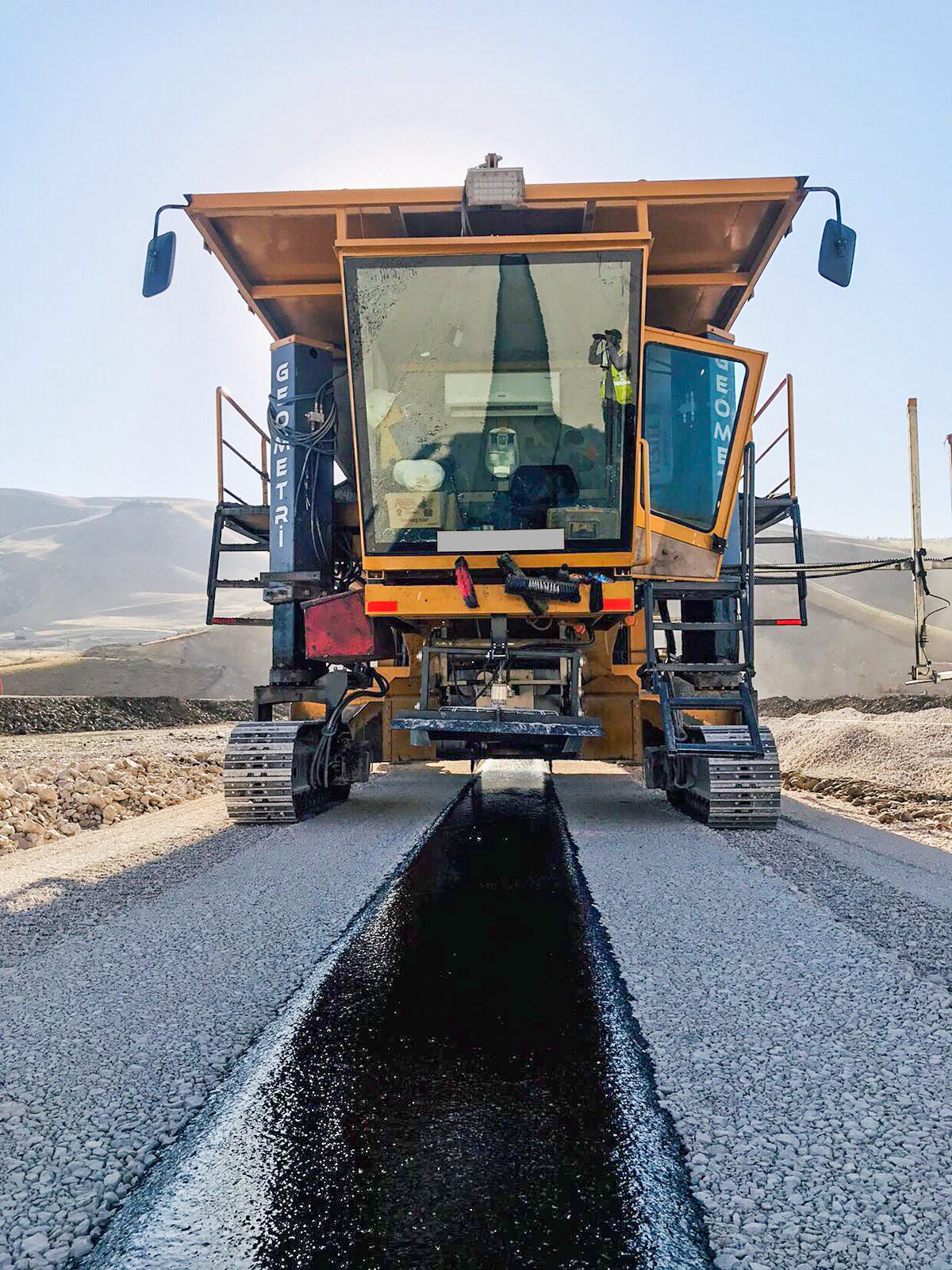

Asphalt core dams play an important role in managing and protecting water resources around the world. Such dams have excellent performance, particularly in terms of seepage control and stability. For example, a study at the Megech Dam in Ethiopia showed that asphalt concrete core dams are more effective in seepage control than clay core dams. In addition, the construction of asphalt core dams is less affected by weather conditions, reducing construction time and therefore costs. Countries such as Europe, Japan, China and Norway have built many such dams over the last 50 years, and now Brazil and Canada are building their first dams. Asphalt-core dams are important not only as an engineering achievement, but also for environmental sustainability; asphalt is a natural, non-toxic material that is ideal for drinking water reservoirs and does not harm the environment. These dams are particularly suitable for dams located in earthquake zones or on compressible soils, as the properties of asphalt concrete can be tailored to specific design criteria. Asphalt core dams offer an innovative and effective solution for managing and protecting water resources around the world.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
